|
| | Le clavecin de Marie-Antoinette |  |
| | | Auteur | Message |
|---|
Le Graveur

Nombre de messages : 20
Date d'inscription : 20/02/2019
 |  Sujet: Le clavecin de Marie-Antoinette Sujet: Le clavecin de Marie-Antoinette  Mer 20 Fév - 23:31 Mer 20 Fév - 23:31 | |
| Le voici  Enfait j'aurais dû mettre un ? parce qu'on n'est pas si sûr, mais dans un titre, non   Le clavecin historique a été réalisé à Anvers, il est signé Johannes Ruckers (le Jeune) et daté 1632 et 1745. En 1884, il a été remis en don au Musée par une famille neuchâteloise. Le clavecin historique a été réalisé à Anvers, il est signé Johannes Ruckers (le Jeune) et daté 1632 et 1745. En 1884, il a été remis en don au Musée par une famille neuchâteloise.
Cet instrument aurait appartenu à Marie-Antoinette, reine de France et épouse de Louis XVI, qui l'aurait donné à une de ses demoiselles d'honneur, Mlle de Trémauville, fiancée du lieutenant neuchâtelois Georges de Montmollin mort aux Tuileries le 10 août 1792 à Paris.
En 1632, le clavecin présente un clavier de 45 notes et 2 registres de jeux de cordes. Soumis à un grand ravalement en 1745 à Paris probablement, il est alors doté de 2 claviers de 58 notes chacun et de 3 jeux de cordes.
Le piètement ainsi que le décor, des fables de Jean de La Fontaine peintes sur feuilles d'or, datent de 1745. La peinture sous le couvercle et une partie de la table d'harmonie appartiennent encore au clavecin de 1632. La générosité du Rotary-Club de Neuchâtel, a permis sa restauration en 1986 à Paris par les Ateliers von Nagel. Depuis, des concerts autour du Ruckers sont proposés au public et des enregistrements sur CD sont produits. https://www.mahn.ch/collections-arts-appliques-ruckers |
|   | | Chakton

Nombre de messages : 1263
Date d'inscription : 22/10/2017
 |  Sujet: Re: Le clavecin de Marie-Antoinette Sujet: Re: Le clavecin de Marie-Antoinette  Mar 26 Fév - 21:09 Mar 26 Fév - 21:09 | |
| Quelques renseignements ne sont pas superflus. 
- The technical definition of a harpsichord is “ a [plucked-string] instrument consisting of a box mounted over legs, together taking the approximate form of a bird’s wing.” (Musica de Regalo)
The composition of the harpsichord is complex and intricate. It includes the main body, containing the pinblock, the soundboard, the hitchpins, the keyboard, and the jack action, as well as the legs and various little parts making it an elaborate musical instrument (Fig. 2). The instrument clavés mostly composed itself of wood; even the keyboards were usually made of wood, instead of ivory. The manufacturing of the harpsichord commenced in the sixteenth century and continued to the seventeenth century. The harpsichord was in high demand until the late eighteenth century when the pianoforte progressively took its place. The main difference between the two is that in the harpsichord the string gets plucked while in the pianoforte a felt hammer comes down on the string, making sounds at different volumes depending on how hard one hits the keys.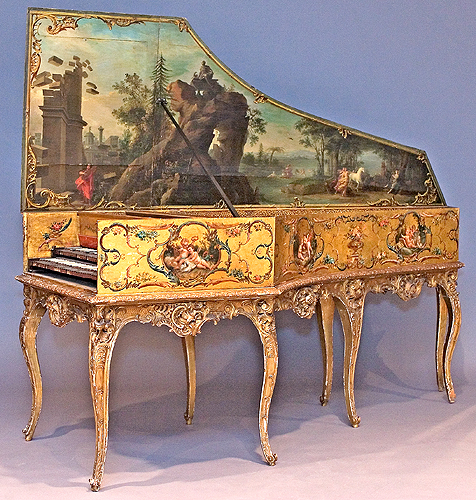  Fig. 1- Harpsichord by Andreas Ruckers, Antwerp, 1643. Fig. 1- Harpsichord by Andreas Ruckers, Antwerp, 1643.Although different countries established their own guilds for producing harpsichords, the Ruckers family was the main and most renowned manufacturers of the string instrument (Fig. 1).Its monopoly of production led it to be characterized as “The Ruckers’ dynasty.” The dynasty took hold when Hans Ruckers joined the Guild of St. Luke in Antwerp (in present day Belgium) as an expert harpsichord constructor. His male progeny, starting with his two sons, also involved themselves in the manufacturing of the harpsichord, as they became the super-power producers of the instrument. 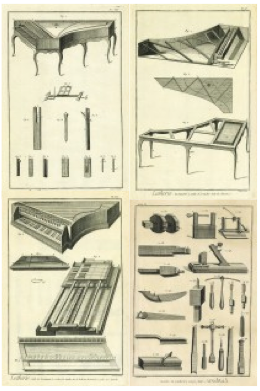 Fig. 2- Encyclopedie, Lutherie, Plate XIV, XV, XVI, XVII. Fig. 2- Encyclopedie, Lutherie, Plate XIV, XV, XVI, XVII.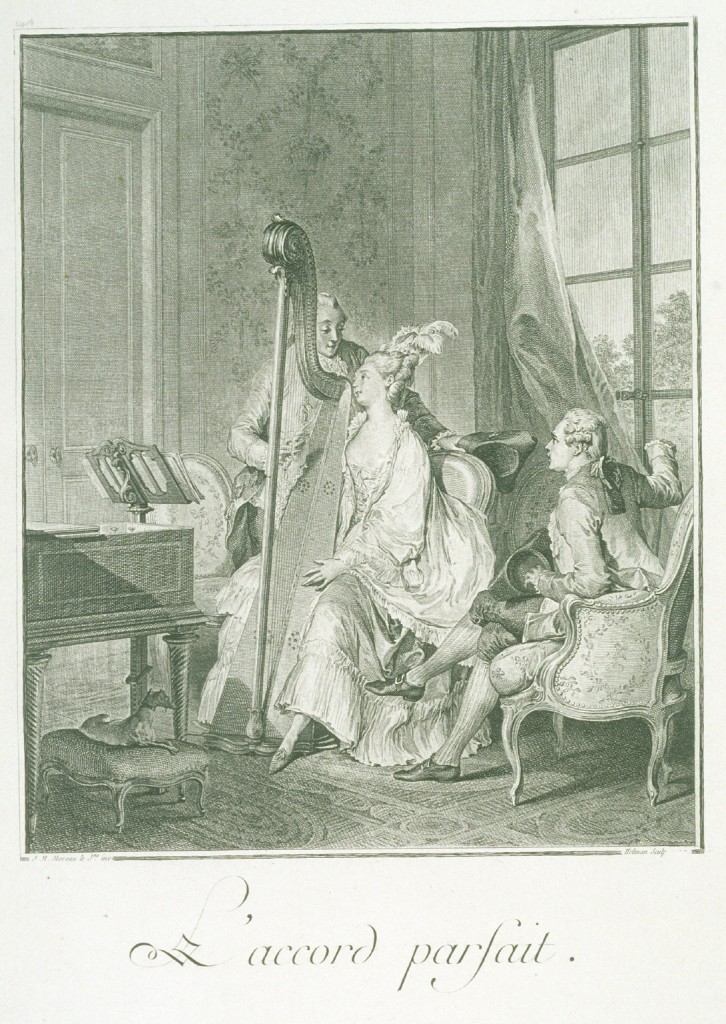 Fig. 3- L'accord Parfait, by Jean Michel Moreau, 1789. Fig. 3- L'accord Parfait, by Jean Michel Moreau, 1789.The Ruckers’ excellence in manufacturing made the harpsichord the “must have” item of the eighteenth century aristocracy all over Europe, and they were exported to Holland, Germany, France, England, Spain, and even Colombia and Peru. The importance of the harpsichord in the 18thcentury French aristocratic society is showcased in Jean Michel Moreau’s etching L’accord Parfait (Fig. 3). Though not the main focus , the harpsichord sits prominently in the music room. The harpsichord was particularly popular at the Austrian court. It was built into l’apprentissage of the royal children. The portrait of L’Archduchesse Marie-Josèphe D’Autriche (Fig. 4) drawn for Maria Theresa as a keepsake when she traveled, shows the young Archduchess at a harpsichord. Eleven portraits were done, depicting her children taking part in court activities relevant to their courtly education. The portrait of Emperor François I’s family (Fig.5), exemplifies to a further extent the role of the harpsichord in the Austrian court. In the portrait, it is in the center of the room as it is being played by the Archduchess, while the men of the family surround it and use it as support. The centrality of the harpsichord shows its importance in the daily life of the Austrian Royal Family.  Fig. 4- Portrait of Marie-Josèphe of Austria, 1762. Fig. 4- Portrait of Marie-Josèphe of Austria, 1762.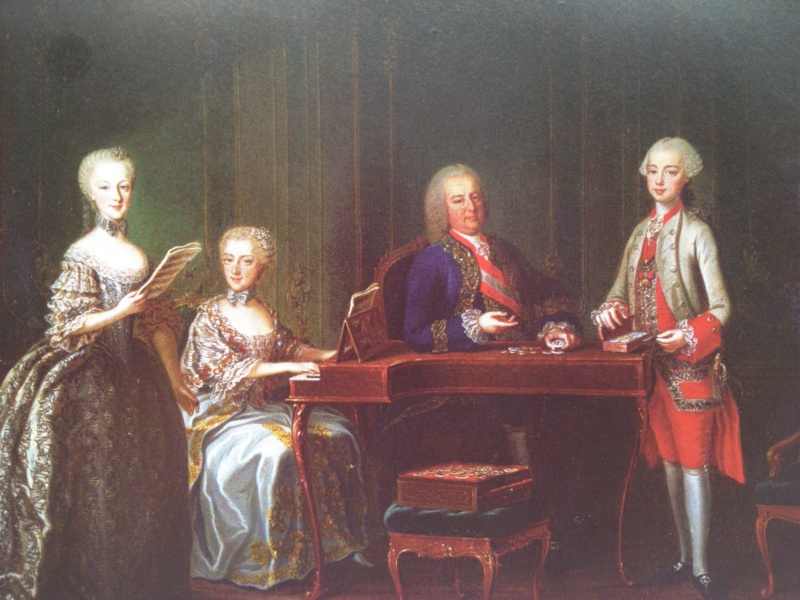 Fig.5- L'Empereur François I, 1763. Fig.5- L'Empereur François I, 1763.The harpsichord was also part of a grander scheme of things: it was part of the “art of motion.” All aristocratic children were required to learn how to move, sit, walk, and ultimately dance. The music of the harpsichord gave the motion a script to follow. It gave fluidity to motion as the aristocrats danced at their private balls. As well as being an accompaniment to motion and elegant movement, playing the harpsichord was a leisurely act. Playing was a time of pleasure and enjoyment. The role of this divertissement in court society is evident in the portrait of Marie Antonia at the Harpsichord in Schonbrünn (Fig. 6). She is enjoying a nice quiet moment to herself while playing music. Although the sons of the royal couple were known to play instruments while the daughters sang, the harpsichord was usually the instrument of choice of young ladies, as the portraits of Marie Antoinette and Marie-Josèphe show (Fig. 4 & 5).  Fig. 6- Portrait of Marie Antoinette at the Harpsichord, 1769. Fig. 6- Portrait of Marie Antoinette at the Harpsichord, 1769.The evolution of the harpsichord coincides with that of Marie Antoinette. As a young Austrian girl she played the harpsichord (Fig. 5) and as the Queen of France she played the pianoforte (Fig. 7). Even though harpsichords were no longer being played, they were kept as valuable historic pieces.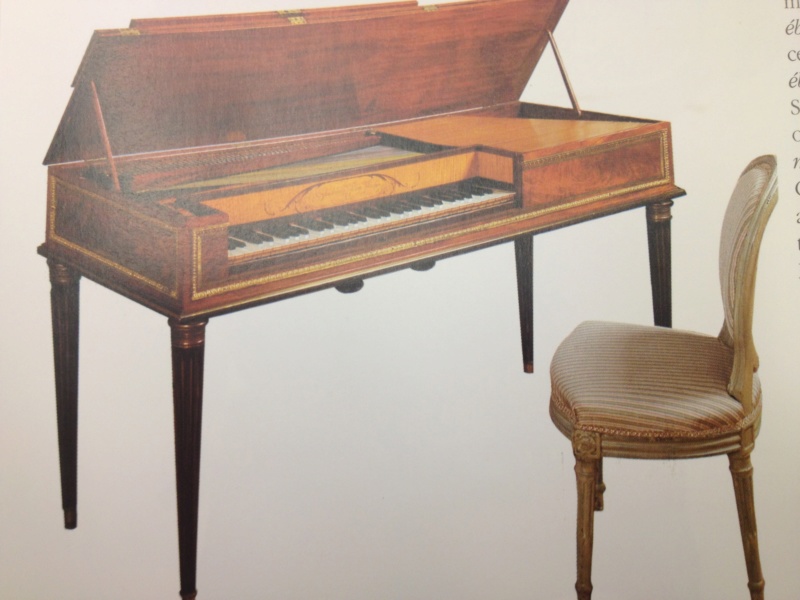  Fig. 7- Pianoforte thought to be Marie Antoinette's. Fig. 7- Pianoforte thought to be Marie Antoinette's.https://sophia.smith.edu/blog/fys199-01f12/luxury-objects-in-the-age-of-marie-antoinette/the-harpsichord/
_________________
X est la force deux fois pure
|
|   | | | | Le clavecin de Marie-Antoinette |  |
|
Sujets similaires |  |
|
| | Permission de ce forum: | Vous ne pouvez pas répondre aux sujets dans ce forum
| |
| |
| |
